Many people need to know what is normal blood sugar level. They may have to watch their glucose level because they are diabetic, or they are athletes who have to watch their diet carefully in order to be ready for training and exercise. People who are required to fast, for medical or religious reasons, also need to monitor their blood sugar levels so that they do not become unwell during their fasting period.
 An average person’s blood sugar level will fluctuate throughout the day. The causes of the fluctuations are related to durations between meals, the content of each meal and the activities that the person performs during the day. Stating what is the normal blood sugar level is difficult because it is different for everyone and even one person’s blood sugar level may fluctuate during the day. However, a cautious medical professional might say that the normal range for glucose in the bloodstream is somewhere around 120 milligrams per deciliter. However, many people will have a normal range somewhere below or above that.
An average person’s blood sugar level will fluctuate throughout the day. The causes of the fluctuations are related to durations between meals, the content of each meal and the activities that the person performs during the day. Stating what is the normal blood sugar level is difficult because it is different for everyone and even one person’s blood sugar level may fluctuate during the day. However, a cautious medical professional might say that the normal range for glucose in the bloodstream is somewhere around 120 milligrams per deciliter. However, many people will have a normal range somewhere below or above that.
The amount of sugar in a person’s blood will rise after they eat and fall as they go without food. Typically, a normal blood glucose reading after eating will go as high as 140 milligrams per deciliter. The rate at which glucose levels rise depends on the content of the food. The rate of the fall of blood sugar levels is usually constant for a person with no illnesses. However, a diabetic often suffers from erratic descents in glucose levels.
A person who is fasting for a period of ten or twelve hours should display a blood glucose reading of around 90 milligrams per deciliter. If they have a higher reading at the end of that period, then doctors may become concerned about the person’s ability to control their blood sugar levels. The same can be said for someone whose blood sugar level plummets rapidly after a short period of fasting. These symptoms are often signs of diabetes.
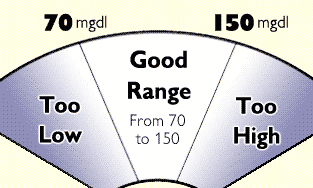
Perhaps a better way to view the subject is to discuss the known extremes. While the blood sugar levels of average people may fluctuate considerably, there are highs and lows which doctors can identify as dangerous. There are also easily identifiable symptoms which accompany these highs and lows.
Low blood glucose levels are diagnosed when the person’s blood glucose reading suggest that they only have around 60 to 70 milligrams of sugar per deciliter in their blood. This low level can cause a person to tremble, feel cold and lose energy. If the blood glucose level drops much below this, then symptoms may worsen and the person could go into shock or even enter a coma.
High blood sugar levels occur when the blood glucose reading moves above the 160 milligrams per deciliter mark. The symptoms are not immediately as severe for the individual, but the long-term effects include damage to organs such as the heart, kidneys and liver. Blood sugar levels that are either too high or too low should be treated immediately.