Monitoring blood sugar levels is essential for individuals living with diabetes to manage their condition effectively. One crucial tool in diabetes management is the A1C test, which provides valuable insights into long-term blood glucose control. By utilizing an A1C levels chart, individuals can track their A1C results over time, gain a better understanding of their diabetes management, and make informed decisions about their treatment plan. In this article, we will explore the significance of the A1C test and how an A1C levels chart can be a useful tool in monitoring diabetes.
Understanding the A1C Test
The A1C test, also known as the hemoglobin A1C test, measures the average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. It reflects the percentage of hemoglobin (a protein in red blood cells) that is glycated or bound to glucose. The higher the blood glucose levels, the more glucose binds to hemoglobin, resulting in an elevated A1C value. By measuring the percentage of glycated hemoglobin, the A1C test provides an assessment of long-term blood sugar control.
Excellent A1C Levels Chart sources of info: Fill out your own A1C chart and info from Mayo Clinic on the A1C test
The Importance of Monitoring A1C Levels
Regular monitoring of A1C levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes for several reasons:
Diabetes Management Assessment: A1C levels provide valuable information on how well diabetes management strategies are working over time. By tracking changes in A1C values, individuals and healthcare professionals can assess the effectiveness of treatment plans, including medication adjustments, lifestyle modifications, and dietary changes.
Treatment Decision-Making: A1C levels serve as a guide for healthcare providers when making decisions about treatment options. Based on the A1C results, adjustments can be made to medication dosages or treatment plans to optimize blood sugar control and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Goal Setting: A1C levels help individuals with diabetes set realistic blood sugar targets. Collaborating with healthcare professionals, individuals can establish personalized A1C goals that are appropriate for their specific needs, age, overall health, and diabetes type.
Using an A1C Levels Chart
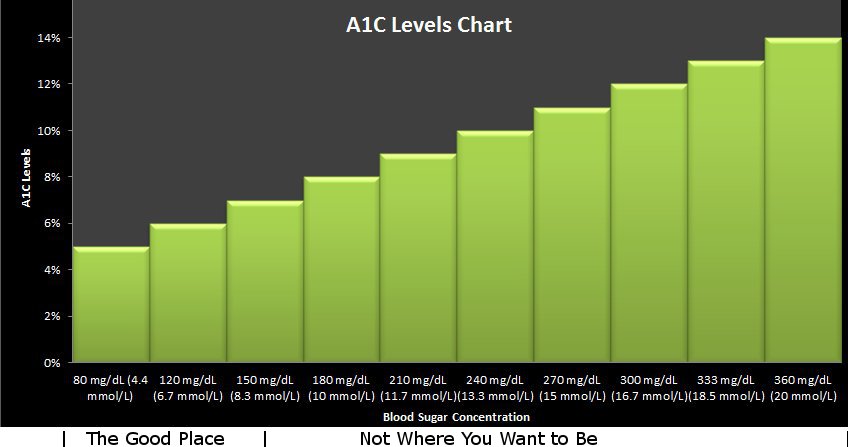
An A1C levels chart is a visual representation of A1C values and corresponding average blood glucose levels. It allows individuals with diabetes to interpret their A1C test results and understand their blood sugar control within a broader context. Here’s how to use an A1C levels chart effectively:
Interpretation of A1C Results: The chart typically presents A1C values as a percentage and correlates them with an average blood glucose range. For example, an A1C value of 7% corresponds to an average blood glucose level of approximately 154 mg/dL (8.6 mmol/L). By referencing the chart, individuals can understand their overall blood sugar control based on their A1C results.
Tracking Progress: By consistently monitoring A1C levels and documenting them on the chart, individuals can observe trends and patterns over time. This enables them to assess whether their diabetes management strategies are effective or if adjustments need to be made. Monitoring progress can serve as motivation and provide a sense of accomplishment when A1C levels improve.
Goal Setting and Discussions with Healthcare Providers: An A1C levels chart facilitates conversations with healthcare providers about goal setting and treatment plans. By discussing A1C results and comparing them to target ranges, individuals and healthcare professionals can collaboratively set realistic goals and make adjustments to optimize blood sugar control.
Testing What You Learned
Utilizing an A1C levels chart is a valuable tool for individuals with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar control effectively. By tracking A1C results over time, individuals can gain insights into their diabetes management, set realistic goals, and make informed decisions in consultation with healthcare professionals. Remember that the